The Viz Engine Render Pipeline focuses on rendering photorealistic scenes. In some cases, the physically-based rendering (PBR) material is too complex. For such scenarios, the Phong material was added. This material type is less complex, has similar properties to the known classic materials, and is usable without a proper light setup, which makes it easy to use for simple 3D geometries and all 2D graphics like lower thirds.
Similar to the PBR material, this material is only usable in the Viz Engine Rendering Pipeline and can be added to a container by right-clicking and select Add Phong Material (Viz Engine Pipeline) which adds a default Phong material to your object. The Phong material is based on the material definition and has the same functionality in Graphic Hub as the PBR material.
Color
Defines the basic color. Diffuse and specular channels get multiplied to this channel. If a texture is going to be used, the base color can be kept white, unless you want to recolor your image.
Alpha information on textures can be used, but only on the Basecolor component. All other maps discard the alpha information.
White Basecolor |
|---|
Blue Basecolor |
White Basecolor + Texture |
Ambient
The ambient component is used to mimic global illumination by giving it a base color that is present in the scene and unaffected by any other light. As this component is always added to the final color, it should be used with low intensity.
White Basecolor | White Basecolor + Texture |
|---|---|
Diffuse
Defines the color of the reflection of incident light in all directions from a surface, so that diffuse illumination of a surface is independent of the camera position.
White Basecolor | White Basecolor + Texture |
|---|---|
Specular
White Basecolor |
|---|
White Basecolor + Texture |
White Basecolor + Texture |
The specular component defines the mirror-like reflection of light rays from a surface. It is only visible if reflections on the surface of the light directly hit the camera. This shininess factor affects the specular channel and controls the sharpness of the specular effect. Small values create flat/smooth highlights and higher values create sharp highlights.
Emissive
The emissive color is used to color parts of the surface which should act like they are emitting light. This can be useful to create glow effects in combination with the bloom post-processing effect.
White Basecolor | White Basecolor + Texture |
|---|---|
|
Final Result
Every component added together gives the final material look.
Base Color |
|---|
Ambient |
Diffuse |
Specular |
|---|
Emissive |
Final Result |
Unlit
Similar to the classic material, the lighting can be disabled. This means that no scene lights affect the material. This is usually desired for 2D objects and is controlled by the Lit checkbox. Unlit materials are defined by the color channel and the emissive channel.
In Unlit mode, it's possible that the geometry also receives shadows. This is controlled by the Shadow checkbox. In Lit mode, shadows are always visible.
Unlit w/o Shadows |
|---|
Unlit with Shadows |
Lit |
Reflectivity
The Reflective property defines if the material is able to reflect its surroundings. It has the same limitations as the screen space reflection. It can only reflect areas, that are rendered. Parts that are invisible to the camera, can not be reflected.
Alpha
Similar to the PBR material, the alpha can be controlled with the Alpha plug-in. Also, the color channel alpha value is taken into account.
25% |
|---|
50% |
75% |
100% |
Texture Generation
Besides using the texture coordinates from the geometry, it is also possible to automatically generate them.
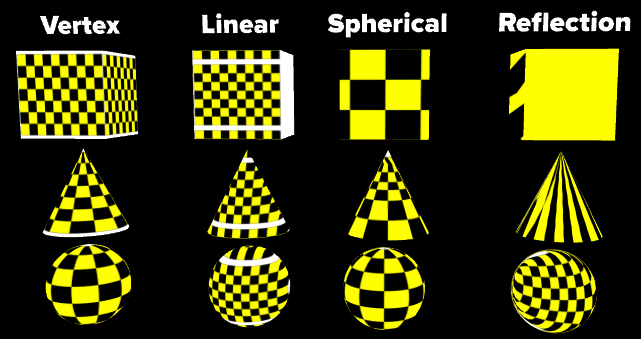
There are four modes to describe how the texture coordinates are organized:
Vertex: Uses the texture coordinates from geometry.
Linear: Uses the linear projection of texture coordinates.
Spherical: Uses the spherical projection of texture coordinates.
Reflection: Uses the texture coordinates from the reflection vector of the surface.
Additionally, texture coordinates can be transformed by the following properties:
Position: Shifts the texture coordinates along the global axis of the texture.
Offset: Shifts the texture coordinates along the local axis of the texture after the rotation.
Rotation: Rotates texture coordinates.
X (only available in Linear mode): Stretches or squeezes texture coordinates vertically, as if it is rotated around the global horizontal axis of the texture.
Y (only available in Linear mode): Stretches or squeezes texture coordinates horizontally, as if it is rotated around the global vertical axis of the texture.
Z: Rotates on the texture plane.
Scaling: Stretches or squeezes texture coordinates along the local axis of the texture after the rotation.
Preserve aspect ratio (only available in Linear and Reflection modes): Preserves the textures aspect ratio on the 1:1:1-scaled geometry.
Advanced properties:
Rotation Pivot: Sets the center where texture coordinates rotate around.
Scaling Pivot: Sets the center where texture coordinates stretch from or squeeze towards by scaling.
Pre-rotation Scaling Factors: Stretches or squeezes texture coordinates along the global axis of the texture.
Pre-rotation Scaling Pivot: Sets the center where texture coordinates stretch away by pre-rotation scaling.
Using Linear mode with Rectangle: To use the texture with Rectangle in Linear mode, given that the Preserve aspect ratio is enabled, the Position needs to be initialized to (0.5, 0.5) first to make the texture appear at the center of the Rectangle.
Clamping
Textures can be set to clamp to a border color. This means instead of repeating the last pixels, they can be overridden by a border color. This can be set by using the Wrapping mode in U and/or V:
Repeat Mode | |
|---|---|
Clamp Mode | |
Clamp to Border |
Information: The Alpha mode of the border currently only works for RGBA images