
Viz Vectar Plus User Guide
Version 1.2 | Published April 12, 2022 ©
Configuring Audio
Working with Audio Levels
Audio Meter
-
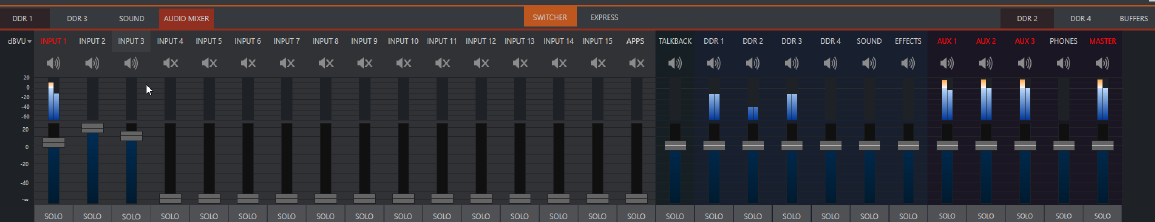
Click the AUDIO MIXER tab for audio features and configuration controls for all internal and external audio sources and outputs, including streaming.
In addition to internal sources and outputs, the Audio Mixer supports sixteen external multichannel audio connections, each channel can be assigned to an extensive list of audio source types.
Each input and output has its own control column with volume slider, VU meter, control features and an identifying label at the top.
To configure an audio mixer channel
-
Roll the mouse pointer over the label to reveal the Configuration button (gear).
-
Click to open a configuration panel for this input.
-
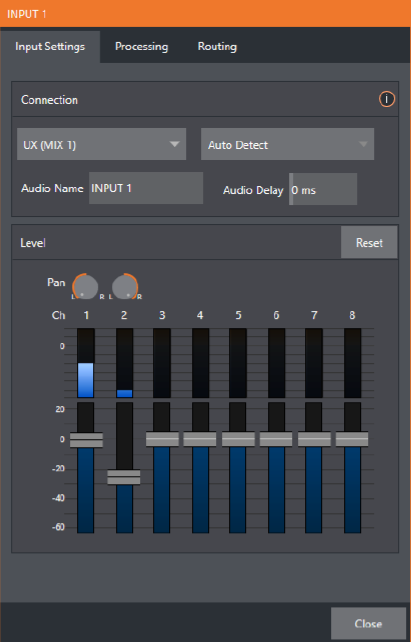
Click the Input Settings tab to display options for an input. Local inputs are listed in the Local group as Input 1, Input 2, etc.).
Note: Analog audio levels conform to SMPTE RP-155. The maximum input/output level is +24 dBu and the sample rate is 48 kHz.
-
(Optional) Assign the input to sound delivered over the network from any NDI or other supported network audio source (such as Audinate’s Dante™ sources; requires a third-party driver) available on the system.
-
A single multi-channel volume fader appears below the VU meter for each source and output.
On first launch these are at minimum gain level.
After adding sources, adjust the faders as required.
Tip: Most numeric controls in this panel can be reset to their defaults using SHIFT + double-click on the control knob. The default value for Gain sliders is 0dBVU.
Audio Headroom
Recommendations
In digital audio systems, levels exceeding legal values are clipped (uniformly assigned the maximum value). This results in audible issues that cannot be easily corrected later.
-
Configure normal operating level (also referred to as the alignment level, and sometimes, nominal level) well below the clipping limit – sufficiently so that occasional excessively loud sounds (say, loud laughter or applause) can be accommodated without risk.
This range above between nominal level and the highest possible level is referred to as audio headroom. What is considered a suitable headroom allowance can vary from one locale to another, in different industry applications, and even in individual studios.
Advanced Settings
Viz Vectar Plus conforms to established audio conventions, providing 20dB of headroom above nominal level (+4dBu at 0dB on the VU scale).
Tip: Be aware that different calibration scales exist within audio technology, among different device types and software. For example, analog mixers commonly show levels on VU scales. Digital devices and editing software usually display levels in dBFS (Decibels Full Scale) with 0dBFS – the absolute maximum signal level that can be recorded – at the top.
-
VU meters have selectable indexing, allowing you to view a traditional dB VU scale or dBFS as you please (see Output and Primary Bus Controls).
-
Whatever scale you choose, use volume controls (and, for mic connections, the gain controls in the Input Settings panel) to avoid over-modulation.
-
The Compressor/Limiter feature (on the Processing tab) is another powerful tool to help you prevent clipping (see Advanced Configuration).